In-Depth Overview of Azure Availability Set
As with on-premises datacenters, planned maintenance operations and potential hardware faults must be considered when deploying resources over the cloud. Therefore, a proper organization of virtual machines becomes essential to avoid or minimize service disruption time. To that end, Microsoft Azure Availability Sets allow administrators to group resources to optimize the execution of maintenance tasks.
Definition of Azure Availability Set
When you deploy new virtual machines (VMs), Azure, by default, does not possess the necessary information to identify dependencies among them. Hence, this may lead to a single point of failure in the hosted service due to an unexpected hardware fault or a maintenance operation.
An Azure Availability Set is a logical grouping capability that guarantees that the VMs included in the same group are isolated from each other. Availability Sets are based on two logical groupings: fault domains and update domains.
- VMs in the same fault domain share common power and network resources, similar to a rack at an on-premises datacenter.
- VMs belonging to the same update domain group can undergo planned and unplanned maintenance and simultaneous reboots. This configuration covers 99.95% of service-level agreements (SLAs).
When working with Availability Sets, a best practice is to create one Availability Set per workload, understanding the workload as a set of servers that work together running the same service (for example, Active Directory Domain Controllers).
Availability Sets and Availability Zones: What’s the Difference?
Depending on the SLAs required by different organizations, Azure includes different options for building and configuring high availability solutions. Availability Zones are unique physical locations within an Azure Region (set of datacenters). Each zone comprises one or more data centers equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking resources.
The main difference between Availability Zones and Availability Sets is that Availability Zones protect your resources from a potential datacenter failure. In contrast, Availability Sets only offer protection from hardware failures within a datacenter, thus increasing SLA coverage from 99.95% to 99.99%.
Steps to Set Up an Availability Set in Azure
To configure an Availability Set in Azure, two steps are required: creating the Availability Set and the assignment of VMs.
Create an Availability Set
To create an availability Set from the Azure portal, follow these steps:
- Log on to your Azure account.
- Click on Create a Resource, search for Availability Set, and click on the Create button.
- Fill in the Subscription, Resource Group, Name, and Region fields according to your requirements. Next, specify the number of fault domains and update domains needed for this Availability Set. Azure automatically manages the distribution of virtual machines among the created domains, always ensuring the best possible configuration within a group. For this example, we configure two fault domains and two update domains.
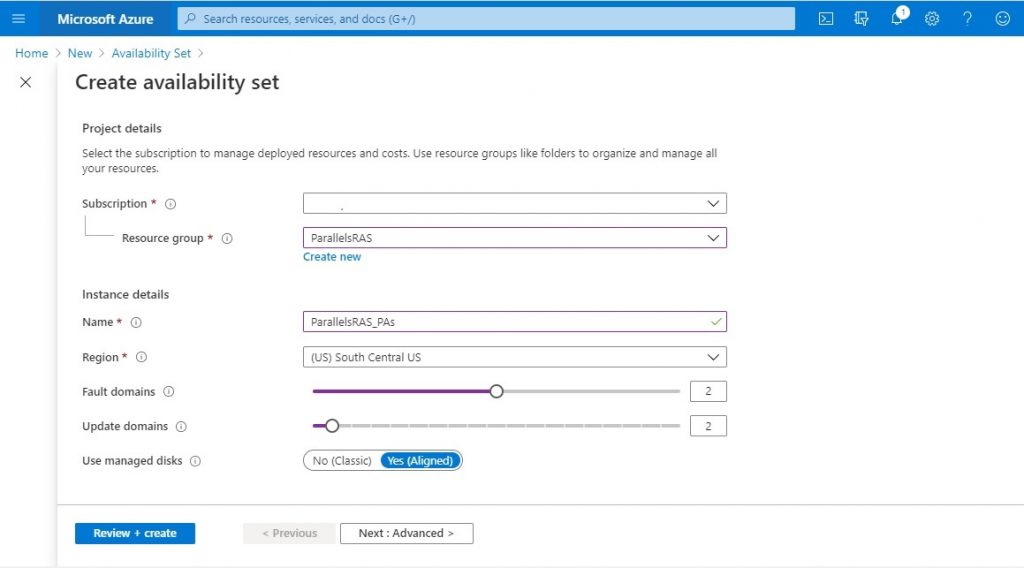
- Click on the Review + create button. Once the validation process is complete, click on the Create button.
- Once the deployment is complete, you can explore the resource and review its features before assigning new virtual machines.
Availability Sets can also be created using Azure PowerShell.
Assign a Virtual Machine
You assign a VM to an Availability Set through the Create a virtual machine wizard. Under the Basics tab, locate the Availability options field. Select Availability set from the drop-down list, and choose the Availability Set resource needed for the VM being created. Complete the rest of the configuration fields according to your requirements.
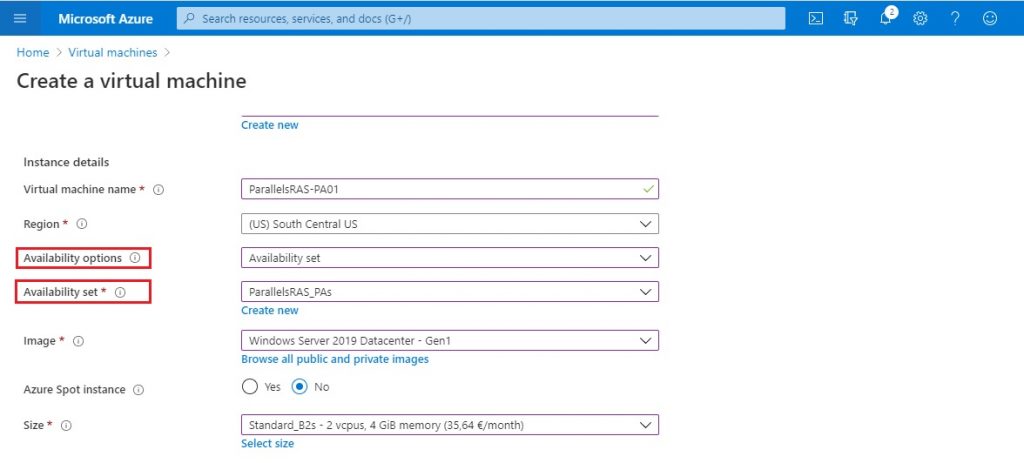
Important things to note are that VMs can be included in an Availability Set only when deployed (existing machines cannot be assigned to an Availability Set). The Availability Set of a virtual machine can’t be changed after being created.
Read more regarding how Azure distributes virtual machines among existing fault and update domains.
Parallels RAS on Microsoft Azure
Parallels® Remote Application Server (RAS) supports hybrid and cloud deployments on Microsoft Azure. Organizations can increase the flexibility and reliability of their Parallels RAS solution by combining Azure native resources. This includes Azure Load Balancer, to load balance the front-end traffic and Availability Sets for the Parallels RAS Secure Client Gateways and Parallels RAS Publishing Agents.
Parallels RAS supports Microsoft Azure Hypervisor as a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) provider, enhancing flexibility and scalability to provision and scale VDI and Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH) workloads on-demand rendering faster deployments and simplifying management. In combination with Parallels RAS auto-scaling and auto-provisioning features, organizations can optimize their resource usage, which is very important for reducing unnecessary costs when working with cloud providers.
What’s more, it’s cost-effective combining Parallels RAS with Azure—IT departments can repurpose a sizable amount of their budget to other pressing projects.
Want to try it out for yourself?

