Alternate Shell RDP Feature | Understanding RDP Architecture
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a network connection protocol created by Microsoft which is designed to provide graphical remote access to Windows-based machines using a Remote Desktop client. This blog post describes how RDP works and introduces one of its multiple configurable settings, the alternate shell RDP feature. Additionally, it outlines how Parallels® Remote Application Server (RAS) reduces costs and management complexity when deploying VDI solutions.
Understanding RDP and Its Uses
Microsoft Remote Desktop clients provide capabilities to use and control a Windows-based PC remotely, thereby you can perform all actions that you would usually do with your physical PC. This includes using installed applications, managing files and folders, and accessing network resources. Locally installed peripherals, including the keyboard, the mouse and the printers, are shared with the remote PC, thus allowing you to use them as if they were connected directly to it.
RDP is commonly used by IT departments for administrative tasks when working with Windows Server machines, but it can also be used by end users to establish a remote connection with their workstations under certain scenarios. For instance, due to the circumstances generated by the pandemic, many companies maintained business continuity by providing their employees with RDP access to their workstations.
Understanding the Architecture for Delivering RDP
RDP is a multi-channel capable protocol, encapsulated and encrypted within the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). The network traffic exchanged between the server and the client during an RDP connection is transmitted within separated virtual channels and includes presentation data, serial device communication, licensing information, and highly encrypted data such as mouse or keyboard activity.
The RDP client initiates a connection to the RDP server through the 3389 TCP port. The RDP server listener thread detects a new session request and generates a new RDP stack instance to handle it. Once the connection is established, the RDP server uses its own video driver to render and construct the display output which will be sent to the client. When the RDP client receives this information, it launches the corresponding Microsoft Windows graphics device interface (GDI) API calls. Client mouse and keyboard events are redirected from the client to the server, which will use its own keyboard and mouse drivers to run these inputs.
Launching an Application through RDP Using the Alternate Shell Option
There are many different features that can be configured when editing the RDP settings file that is used by the Remote Desktop clients. The alternate shell feature combined with other settings related to RemoteApp are used to specify a program that will be started automatically in the remote session as the shell instead of the explorer. This option may be useful under certain scenarios where you want to open a particular application directly instead of a full desktop.
The steps below create an RDP file that will open Microsoft Paint when connecting to the RDP server:
1. Add applications to or disable the whitelist
RDP Servers are configured by default to only allow running applications included in a whitelist. You can add specific applications to the list or disable the whitelist, thus allowing all applications implicitly.
- Add specific applications:
- Run regedit.exe.
- Navigate to HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Terminal Server\TSAppAllowList\Applications.
- Add a new key for every application you want to grant access. This key must include a string named Name and a string named Path field with the application settings:
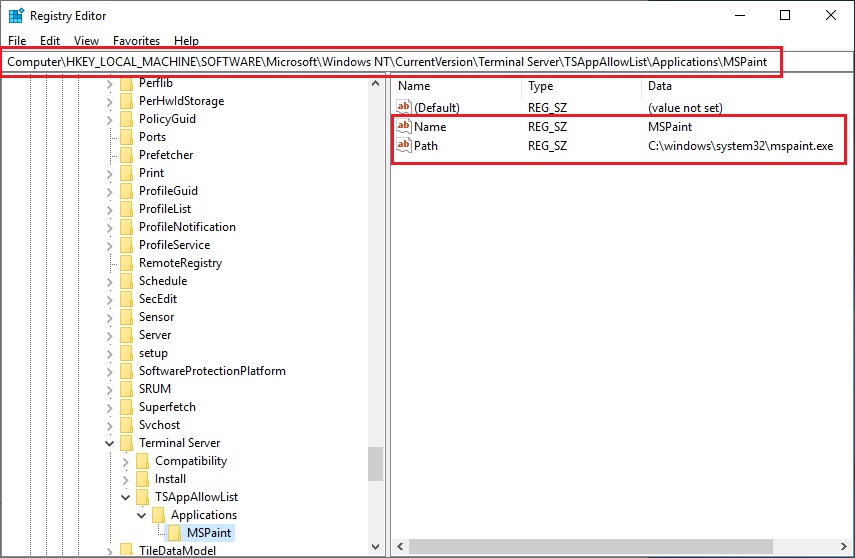
or
- Disable whitelist:
- Run regedit.exe.
- Navigate to HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Terminal Server\TSAppAllowList.
- Locate the fDisableAllowList. Change it from 0 to 1.
Note: For testing this feature, we recommend disabling the whitelist.
2. Open Notepad
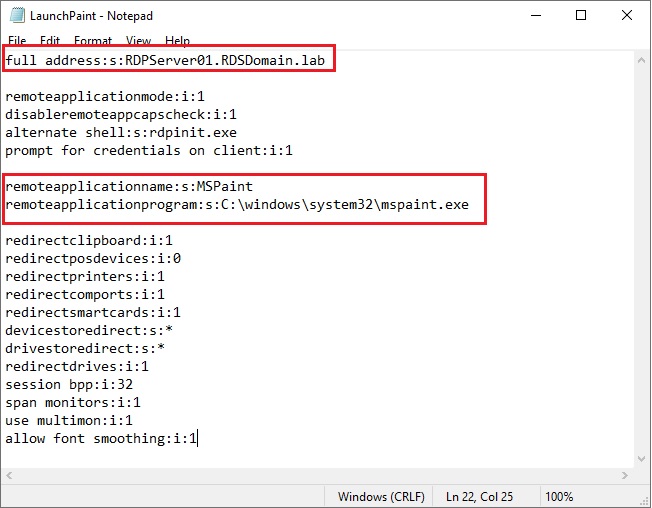
Create a text file with the following:
- full address:s:server.yourdomain.com
- remoteapplicationmode:i:1
- disableremoteappcapscheck:i:1
- alternate shell:s:rdpinit.exe
- prompt for credentials on client:i:1
- remoteapplicationname:s:MSPaint
- remoteapplicationprogram:s:C:\windows\system32\mspaint.exe
- remoteapplicationcmdline:s:
- redirectclipboard:i:1
- redirectposdevices:i:0
- redirectprinters:i:1
- redirectcomports:i:1
- redirectsmartcards:i:1
- devicestoredirect:s:*
- drivestoredirect:s:*
- redirectdrives:i:1
- session bpp:i:32
- span monitors:i:1
- use multimon:i:1
- allow font smoothing:i:1
You need to customize the following settings in the file:
- full address: The network name of your RDP Server.
- remoteapplicationname: The name of the application on the RDP Server.
- remoteapplicationprogram: The path to the application on the RDP server.
- remoteapplicationcmdline: Command-line options for the executable; this is optional.
3. Save the file as a .rdp file
4. Double-click the .rdp file.
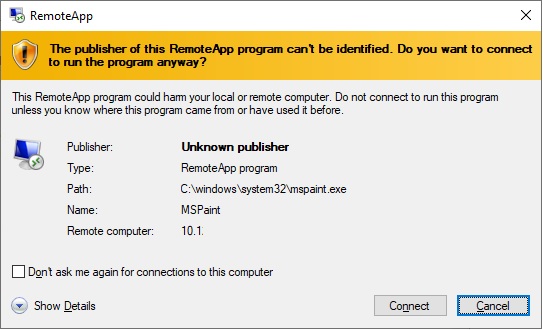
You may receive an unknown publisher warning because the file is not digitally signed. Click on Connect.
5. Enter Credentials and Run Alternate Shell RDP
Next, you will be prompted to enter your user credentials. Enter your username and password, and your alternate shell rdp will run.
Alternate Shell RDP – Simplify VDI Management and Reduce Costs with Parallels RAS
Parallels RAS reduces costs and management complexity when deploying VDI solutions because it has a:
- Straightforward installation: Due to its easy and wizard-driven installation process, Parallels RAS enables organizations to reduce administration complexity while increasing productivity. Parallels RAS provides built-in automation capabilities and includes multiple pre-defined optimizations for VDI, RDSH, and Azure Virtual Desktop workloads.
- All-inclusive single license model: There is only one product edition for on-premises, hybrid, and cloud setups, which provides enterprise-range features such as application and desktop delivery, load balancing, printing, monitoring, and reporting.
- Optimized resource usage: Parallels RAS includes auto-scaling and auto-provisioning features when working with RDSH, VDI, and Azure Virtual Desktop workloads, thus providing companies with on-demand scalability, reduced costs, and optimized resource usage.
Try a free 30-day, full-featured trial of Parallels RAS.
Download the Trial

