What Is ADC Delivery and How Does It Bring Value To IT Organizations?
ADC Delivery
In today’s dynamically changing business world, organizations are required to provide 24/7 access to resources. Speed and efficiency have become an inevitable requirement. With the advent of smartphones, virtual offices have taken a new shape. Moreover, a versatile range of devices have come into the network. Businesses not only have to provide continuous delivery of services to employees and customers, but they also have to cater to a range of platforms and operating systems. Load balancers that handle huge amounts of traffic are a thing of the past; application delivery controllers (ADCs) are the latest trend. Not only does ADC delivery provide high availability load balancing, but it also offers additional features for business networks. According to MarketsandMarkets, the network infrastructure market combining ADC and WAN optimization controllers is expected to reach $5.82 billion by 2020.
An Overview of ADC Delivery
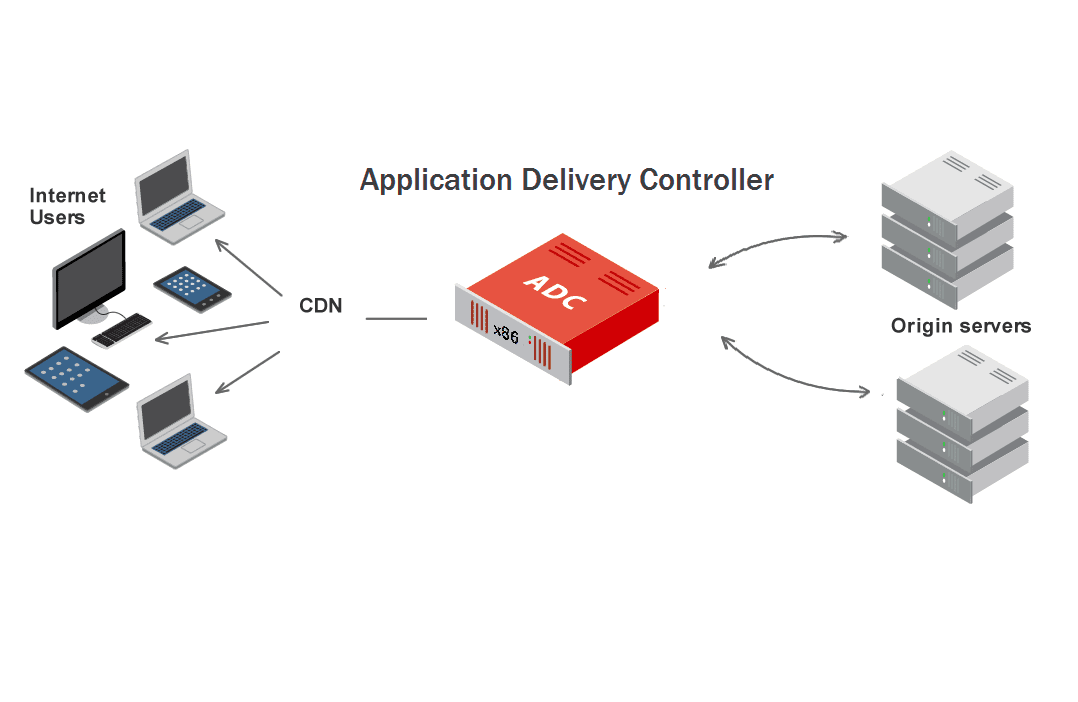
An application delivery controller (ADC) is a network device that is installed in the datacenter to offload network load from servers and optimize the performance of application delivery. Normally, ADCs are installed as front-end to web servers and between the firewall/router and web farm servers. They combine layer 4 load balancing with layer 7 application management to provide a high-performing application delivery solution.
ADCs were initially introduced as load balancing and application acceleration tools in 2004. As businesses realized the different options ADCs offered to networks, they added other features to ADCs. By 2006, ADC delivery had matured, with additional features such as application-layer security, SSL offload, content switching, traffic shaping, compression, and cache added to its portfolio. Combined with WAN optimization solutions, an application delivery network (ADN) now provides comprehensive application delivery solutions to businesses of all sizes.
ADCs have come a long way from their introduction as advanced load balancing tools to now providing a powerful application delivery solution.
Application Delivery to Different Platforms and Devices
With the advent of cloud computing and the mobile revolution, businesses now have to deliver applications to a range of devices including desktops, laptops, and mobile devices. Modern mobile devices come with different OSes and platforms, making it tough for IT administrators to keep up. ADCs enable administrators to efficiently deliver applications to any platform and any device while enabling applications to proactively adapt to different networks and protocols.
Applications are always available
The core functionality of “ADC delivery” is load balancing. The advent of smartphones has allowed employees to access business applications from any location and at any time. With changing business needs, businesses need to dynamically scale up resources to keep applications always available to end-users, day and night. When servers fail in the network, applications hosted on them become inaccessible. Businesses normally add extra servers to bring fault tolerance into their environments. However, ADCs efficiently balance application workloads across a cluster of active servers to provide seamless failover.
ADCs distribute traffic across a cluster of servers. They check for a number of criteria before directing traffic to a specific network and check for keywords or requested file types in the packet headers to determine the exact server to which the traffic should be sent. Powerful virtualization tools such as Parallels Remote Application Server not only check for available servers, but also identify the available gateway for high availability load balancing. Another capability of ADC delivery is that it can send traffic to a cluster of servers located in a different datacenter as well.
Monitoring capabilities of ADCs
ADCs are intelligent devices. They can monitor server operability and health beyond a standard ping. If a server is found to have an issue, ADCs redirect the traffic to another healthy server. In addition, they provide historical and real-time analysis of user and network traffic such as WAN latency, datacenter latency, and bandwidth usage. This analytic information enables the helpdesk team to quickly identify issues and provide a resolution.
Delivering optimized performance
In today’s highly competitive business world, organizations not only have to keep applications available, but they also need to meet user expectations in terms of performance and usability. ADCs perform server offloading on high-latency and mobile networks to deliver an enhanced user experience. SQL database load balancing is another technique wherein the offloading is done at the datacenter level. It uses connection multiplexing, caching, and compression to improve the performance of applications. ADC delivery involves the use of TCP multiplexing to handle high volumes of inbound traffic. Domain sharding is another technique that optimizes application delivery over mobile networks.
Provides enhanced security
As ADCs are the first point of entry, application security is an important concern. ADCs use different mechanisms to provide higher security to networks; an XML-based SAML protocol is one among them. For SaaS-based applications, ADCs use the Active Directory data store to authenticate user credentials. ADCs also use rate-limiting measures to throttle a massive surge of inbound requests and minimize the available bandwidth to prevent DDOS attacks. They combine negative and positive security models such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and signature-based protection to flag malicious requests and effectively block them.
Parallels Remote Application Server (RAS)
Application Delivery Controllers have optimized business resources and improved business performance to provide great value to IT organizations. With business networks turning into application-centric environments, ADCs stand at the forefront of this transformation. The key here is to choose the right tool that can provide comprehensive ADC delivery solutions that are easy to use and significantly cost-effective.
Parallels RAS is not only a virtual application and desktop delivery solution but also provides high availability and resource-based load balancing. It is easy to install and use, provides comprehensive features in a single package and is significantly less expensive than its competitors.
References

