How do DDoS attacks work?
Have you ever been stuck in a traffic jam that blocks an entire highway, making it impossible for everyone to reach their destination?
Then you know what a DDoS attack is like.
Although it doesn't involve cars or highways, a DDoS attack works somewhat similar.
Attackers flood a targeted network, server, or website with traffic flooding, overwhelming its capacity and causing slowdowns, disruptions, or complete outages.
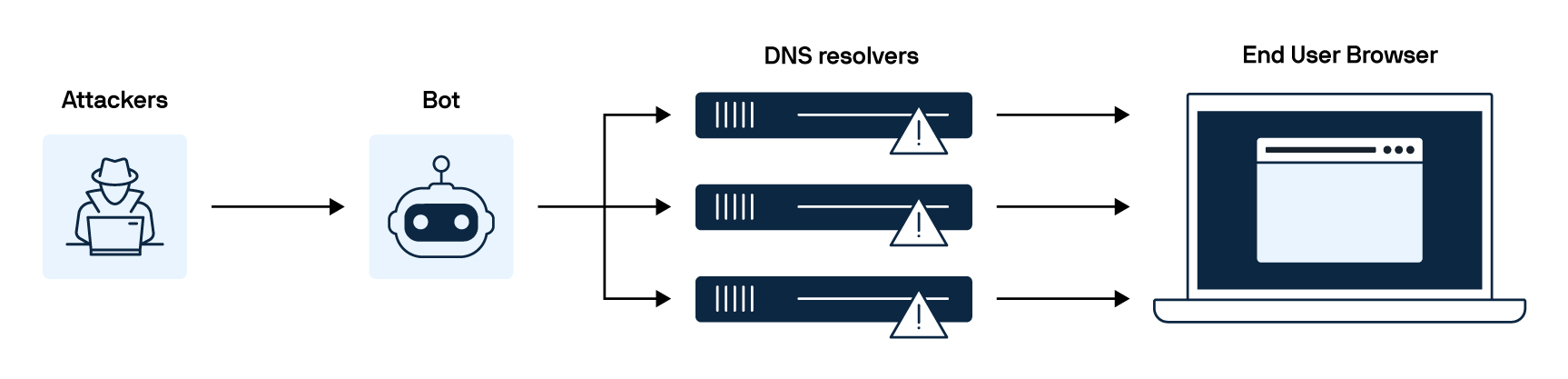
Here's exactly how it works:
The attack army of bots
In order to drive a large amount of traffic, you need a large number of devices.
DDoS attacks typically rely on botnets, a network of compromised devices and servers infected with malware.
Often, these devices, referred to as "bots" or "zombies", have unknowingly been taken over by hackers or cybercriminals.
When the attacker has assembled enough devices to form a botnet, they can command the devices to send overwhelming traffic to the target.
Quickly, that disrupts the target's ability to operate normally.
Overloading the target
To overwhelm a target, attackers use different methods to generate excessive traffic.
These include:
- Volumetric attacks: These flood the target with a massive amount of data, exhausting bandwidth and slowing or shutting down services.
- Protocol attacks: These exploit weaknesses in network protocols, such as SYN floods or DNS amplification, to overload system resources.
- Application layer attacks: These mimic legitimate user behavior, making them harder to detect. Attackers may flood login pages, APIs, or other services with requests, consuming server resources.
By combining these techniques, attackers can make it difficult for even the most robust security measures to keep services online.
The consequences of a DDoS attack
A successful DDoS attack can have severe consequences.
For example, websites and online services can become unavailable to potential customers and users.
This can lead to revenue loss, both due to users not being able to access their resources or complete purchases, and the cost of recovering after an attack.
As a result, an organization's reputation can take a hit as customers' or users' access to services or the website is compromised.
How are DDoS attacks launched?
DDoS attacks are carried out using a coordinated effort to overwhelm a target system with massive amounts of traffic.
Hackers exploit vulnerable devices, turning them into a botnet that floods the target with malicious requests, rendering it unable to function properly.
Learn how a DDoS attack is launched below:
- Hackers launch their infection by spreading malware through phishing emails, malicious downloads, or security vulnerabilities to compromise internet-connected devices.
- The devices form a botnet as the infected machines, now under the attacker's control, are linked together into a large network.
- A large number of requests are sent to the target when the attacker commands the botnet to flood a website, server, or network with overwhelming traffic.
- The target becomes unable to respond to legitimate requests as its resources are consumed, causing slowdowns, crashes, or complete service outages.
12 types of DDoS attacks
DDoS attacks come in various forms, each exploiting different vulnerabilities to overwhelm a target system.
These are some of the most common types of DDoS attacks:
DNS amplification
Attackers send small DNS requests with a spoofed IP address (the target's address), causing DNS servers to return significantly larger responses and overwhelming the target with excessive traffic.
UDP flood
Massive amounts of UDP packets are sent to random ports on the target system, forcing it to check for applications listening on those ports and consume resources until it crashes.
ICMP flood
Also known as a "ping flood," this attack overwhelms a target by sending large volumes of ICMP (ping) requests, exhausting its bandwidth and processing power.
HTTP flood
Attackers send a high number of what appear to be legitimate HTTP requests to a website’s server, consuming resources and making it difficult for real users to access the site.
Protocol attacks
These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in network protocols, such as TCP, UDP, or ICMP, to disrupt services by overloading or crashing network devices.
Slowloris attack
A highly stealthy attack where an attacker keeps multiple connections open to a server by sending partial HTTP requests, preventing it from processing new connections.
Application layer attacks
By targeting specific web applications, these attacks mimic legitimate user interactions to exhaust server resources and cause downtime.
SYN flood
An attacker exploits the TCP handshake process by sending a flood of SYN (synchronization) requests to a server but never completing the handshake, leaving the server’s connection table full.
NTP amplification
Through this attack, attackers exploit Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers by sending small requests with a spoofed IP address, causing the server to respond with a much larger reply to the victim, overwhelming its bandwidth.
Smurf attack
This attack uses ICMP echo requests (pings) sent to a network's broadcast address, tricking devices on the network into flooding the target with responses.
Command and control attack
Command and control (C2 or C&C) attacks involve cybercriminals using a rogue server to issue commands to malware-infected devices and extract stolen data.
Over time, the malware can pivot to other vulnerable systems, forming a botnet that attackers exploit for large-scale cyber threats like DDoS attacks and data exfiltration.
RUDY (R-U-Dead-Yet?)
RUDY is a slow-rate attack that targets web applications by sending tiny, incomplete HTTP POST requests.
Over time, it exhausts server resources, rendering the target unresponsive—hence the name.
8 ways to mitigate the threat of DDoS attacks
A DDoS attack can impact your organization's reputation, revenue, and functionality. Therefore, minimizing the threat of an attack should be a priority.
Below are some of the most effective ways to do so:
1. Load balancers
Load balancers distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers prevents any single server from becoming overwhelmed. Load balancers help maintain service availability during an attack.
2. Traffic filtering
Advanced traffic filtering solutions use AI and machine learning to analyze and block suspicious or malicious traffic before it reaches the target network.
3. Rate limiting
Setting thresholds on the number of requests a user or system can make within a certain time frame helps prevent excessive traffic spikes from overwhelming servers.
4. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs distribute website content across multiple geographically dispersed servers, reducing the strain on the primary server and absorbing large-scale DDoS attacks.
5. Firewalls
Network firewalls monitor and block malicious traffic, filtering out harmful requests before they reach critical systems.
6. Anycast routing
This technique disperses traffic to multiple data centers based on the shortest network path, preventing a single target from being overloaded.
7. DDoS mitigation services
Specialized security providers offer DDoS protection services that detect and mitigate attacks in real-time using cloud-based scrubbing and filtering techniques.
8. Redundant infrastructure
Having backup servers in multiple locations ensures that if one system is affected by an attack, traffic can be redirected to another, maintaining availability.
See how Parallels Browser Isolation can help your organization stay protected from cyberattacks.
How do organizations use Parallels solutions to stay secure and protect themselves from DDoS attacks
You've now learned about the various types of DDoS attacks an organization can fall victim to, and as cybercriminals are only getting smarter, staying secure is top of mind for many organizations.
A remote application server or browser isolation tool can help safeguard organizations, minimize the risk of cyber threats, and mitigating potential consequences if an incident occurs.
By choosing Parallels RAS, Seabix has strengthened its security controls through detailed reports on server usage, devices used, and applications accessed.
Remote work has become secure, while strict data protection measures are maintained for maximum security.
When Vetserve AS switched to Parallels RAS, they saw security improve immediately.
By centralizing data protection and upholding strong security measures, their exposure to a potential cyber attack is reduced.
As talks on cyber threats grew, Plextec found that their clients demanded better protection for cyber insurance compliance.
Recognizing the urgent need for a secure solution, they turned to Parallels RAS.
With the tool's enhanced security controls, including multi-factor authentication and advanced isolation measures, their data protection is improved, enabling uninterrupted remote access.
Parallels Workspace Solutions for mitigating DDoS attacks
The purpose of DDoS attacks is to bring business to a halt. But with Parallels Workspace Solutions, operations continue running. By filtering out malicious traffic, organizations stay connected while threats are neutralized.
Resources
Marching ahead with Parallels Browser Isolation: A note from the SVP of Product
Cyber threats are evolving, and traditional security tools aren’t always enough. Learn more about how Parallels Browser Isolation adds an extra layer of protection, keeping web-based attacks at bay while ensuring secure access to the apps you rely on every day.
Network attacks and cyber security threats
Organizations face growing security threats stretching from DDoS attacks to unauthorized access. Discover how Parallels RAS' built-in security features like multi-factor authentication, TLS encryption, and network segmentation can help keep your systems protected.
How a server failover solution works
A DDoS attack can severely impact your infrastructure, but with the right failover strategy, your business stays online. Parallels RAS offers high availability load balancing (HALB) and real-time monitoring, ensuring traffic is dynamically distributed across healthy servers—even during an attack.
Take the next step with Parallels Browser Isolation
The Parallels ecosystem provides a range of cybersecurity solutions, allowing you to select the product or combination of products that best suits your needs. Take a proactive step towards better cyber security with Parallels Browser Isolation.





